Phishing Attacks
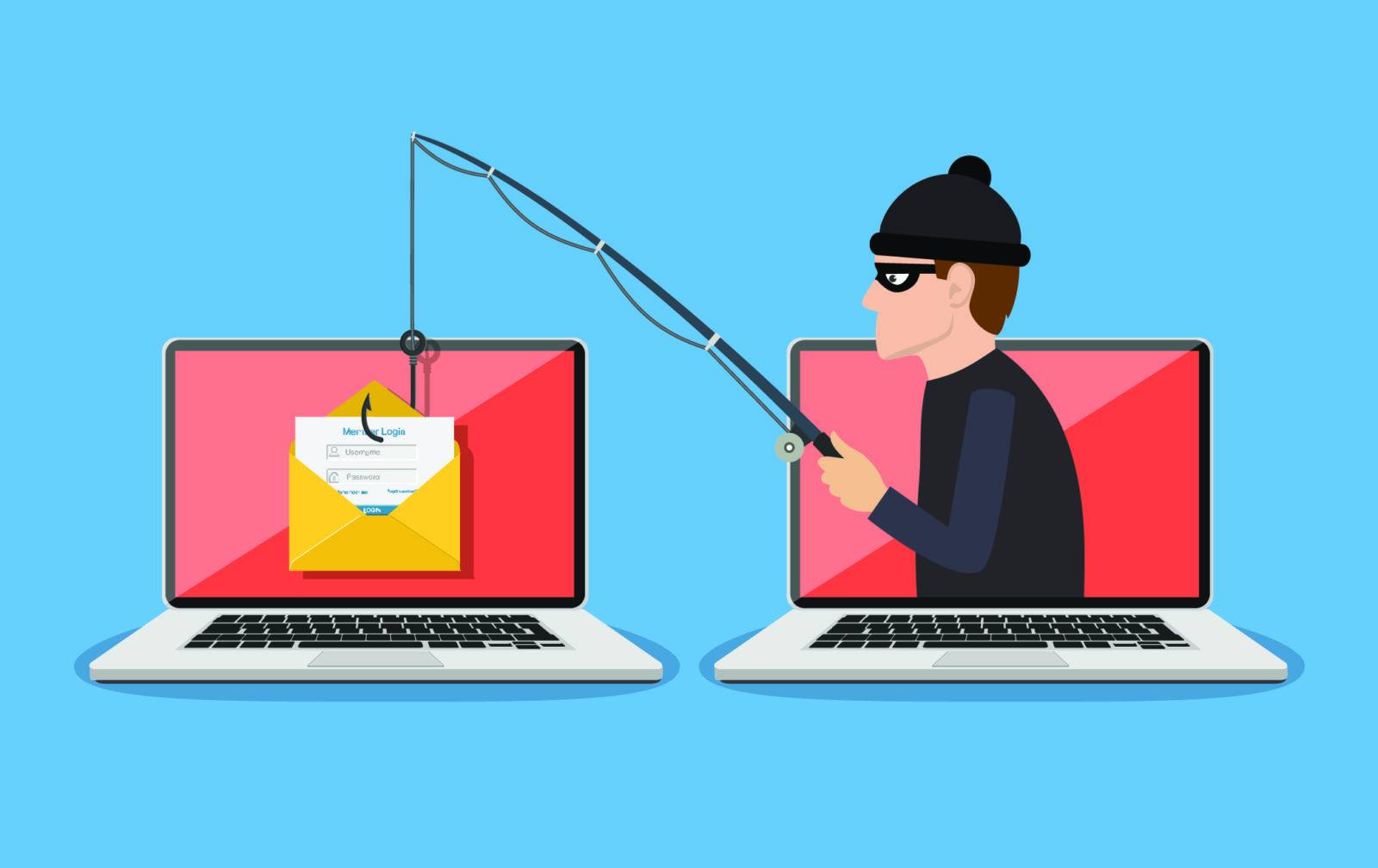

What it is
Phishing is a cyber attack where attackers disguise themselves as trusted organizations to steal sensitive information like passwords or OTPs.
How it works
- Attackers send emails or messages pretending to be legitimate.
- Messages create urgency or fear.
- Victims are redirected to fake websites to steal data.
Examples
- Nepal: Fake OTP requests from local banks.
- International: Large-scale campaigns mimicking PayPal or Google.
How to prevent it
- Never click unknown links or attachments.
- Verify sender addresses carefully.
- Enable multi-factor authentication.




Social Engineering
What it is
Manipulation of people into revealing confidential information or performing unsafe actions.
How it works
How to prevent it